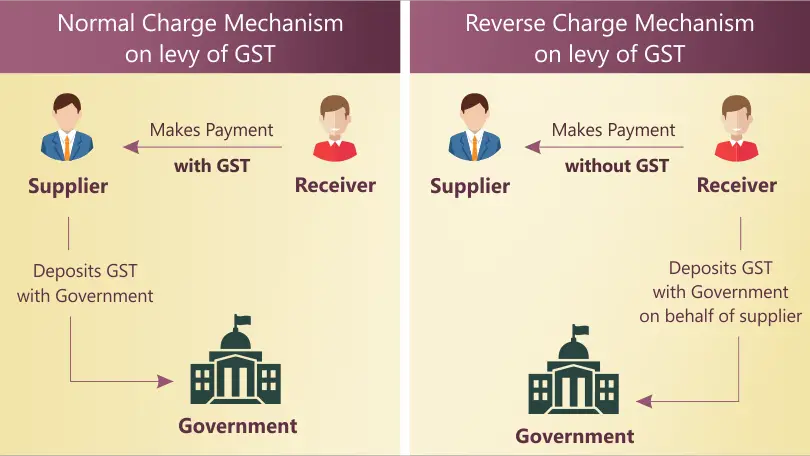
What is Reverse Charge?
Normally, GST is to be collected by the person who is selling good and services. But in some cases GST is to be collected by the purchaser of goods/service and not by seller. This is called Reverse Charge Mechanism, RCM in short.
In some cases of sale through E-commerce operator such as Uber, ola etc the tax is not collected and deposited by seller but collected by e-commerce operator. Such cases are not called reverse charge.
In which Cases RCM is applicable?
Reverse charge is applicable in two cases
- Supply of specific goods or services notified by government [section 9(3)]
- When registered person purchase goods services from unregistered person. Also applicable on composition dealers. [section 9(4)]. This section is postponed till 30th September 2019 via notifications as under
| Notification No. | Summary |
| Notification No.8/2017 – Central Tax (Rate) | This notification exempts RCM under section 9(4) up to Rs. 5000 per day. |
| Notification No. 38/2017 – Central Tax (Rate) | This notification remove limit of rs. 5,000 up to 31 Mar 2018. i.e no RCM under section 9(4) applicable. |
| Notification No. 10/2018 – Central Tax (Rate) | This notification extend date of exemption to 30 June 2018. |
| Notification No. 12/2018 – Central Tax (Rate) | This notification extend date of exemption to 30 Sep 2018. |
| Notification No. 22/2018 – Central Tax (Rate) | This notification extend date to exemption to 30 Sep 2019. |
Purchase from Unregistered Person of any goods/services
When a registered person purchases any goods or services from an unregistered person then such registered person has to pay GST on reverse charge basis. An unregistered dealer can not make inter state sales, therefore such sales is always intra-state sales.
Although the government has given an exemption of Rs. 5,000 per day. Therefore if a total purchase of less than Rs. 5,000 is made in one day from unregistered person then there is no requirement to pay tax on RCM. This limit is total of Rs. 5,000 from all suppliers and not per supplier. Notification No. 8/2017 Central Tax (Rate).
The registered person has to print a self invoice.
Purchase from any person of Specified product/services
For some products/services, reverse charge is specifically provided. In such cases reverse charge is payable by the receiver even if the seller is registered person subject to the conditions specified for such product/service.
The person who is required to pay tax under RCM under this head has to register irrespective of threshold limit.
The seller of services/goods on which covered under this point are required to mention in their tax invoices that GST is payable on reverse charge.
Example – A trader who is registered in GST takes services of Goods Transport Agency (GTA) for Rs. 10,000. This service is listed under the reverse charge list therefore trader has to pay tax @ 18% on Rs. 10,000 on RCM. However such GST paid is also allowed as Input tax credit in same month and therefore net liability of tax will not increase.
A complete list of such goods and services is given at end of this article.
Rate of GST
The rate of tax to be used is the rate which is applicable on such goods/service. GST Compensation Cess is also applicable on reverse charge. If the goods/services purchased in exempted or nil rated then no tax is payable under RCM.
Composition dealers are required to pay reverse charge at normal rates (5%,12%,18%,28%) and not at the composition rates (1% or 5%).
Input tax Credit of GST paid in RCM
Any amount paid as reverse charge is allowed as input tax credit subject to condition that credit is allowed in normal circumstances to such business. For example composition dealers are not allowed to take input tax credit in normal circumstances and therefore they are also not allowed to take input tax credit on gst paid on reverse charge.
Also the amount of GST under Reverse charge is to be paid in cash only and can not be paid from ITC available. The net result is that minimum amount of GST payable in a tax period is the amount of reverse charge in that period.
Advance paid for reverse charge supplies is also leviable to GST. The person making advance payment has to pay tax on reverse charge basis. (This provision is postponed)
Accounting Entries for Reverse Charge
At time of purchasing such goods/ services:
Purchase A/c Dr
Input SGST A/c Dr
Input CGST Ac Dr
To Creditor A/c
To Output SGST RCM A/c
To Output CGST RCM A/c
In case of purchase of asset or expense, specific account will be debited. Output SGST RCM A/c is used in place of normal Output SGST A/c to differentiate both taxes as taxes under RCM can not be adjusted against input taxes and has to be paid in cash.
At time of payment of gst
Output SGST RCM A/c
Output CGST RCM A/c
To Cash/Bank A/c
Invoicing under RCM
A registered person liable to pay tax under reverse charge (both for supplies on which the tax is payable under reverse charge mechanism and supplies received from unregistered persons) has to issue an invoice in respect of goods or service or both received by him. Such a registered person in respect of such supplies also has to issue a payment voucher at the time of making payment to the supplier.
There is no specific format for such self invoicing. The same format which the person is using for invoicing can be used only heading is to be changed.
Registration Requirement
If a person only supplies goods and services on which GST is paid on reverse charge basis then such person is not required to take registration even if the turnover exceeds the specified limits. For example a farmer sells cashew nuts to a trader, trader is liable to pay gst on rcm basis. If farmer is not engaged in trading of other taxable goods then he is not liable to take registration under gst. (Notification No. 5/2017 – Central Tax )
Time of Supply (Date on which RCM Tax is Payable)
For the levy of Reverse Charge under GST, it is very important to ascertain the time of supply as GST would be required to be deposited with the Govt within 20 days from the end of the month in which the services were provided.
Time of supply in case of supply of Goods
In case of Reverse Charge, the time of supply would be the earliest of the following
- The date of receipt of goods, or
- The date of payment, or
- The date immediately after 30 days from the date of issue of invoice by the supplier.
If it is not possible to determine the time of supply under (a), (b) or (c) above, the time of supply shall be the date of entry in the books of accounts of the recipient.
Time of supply in case of supply of Services
In case of Reverse Charge, the time of supply would be the earliest of the following
- The date of payment, or
- The date immediately after 60 days from the date of issue of invoice by the supplier.
If it is not possible to determine the time of supply under (a) or (b) above, the time of supply shall be the date of entry in the books of accounts of the recipient.
Date of Payment
For the purpose of computation of Date of Supply, the Date of Payment shall be earlier of the following:-
- The date on which the payment is debited from his bank account or
- The date on which the recipient entered the payment in his books
List of services on which GST is payable on reverse charge
| Sl. No. | Service | Provider of service | Percentage of service tax payable by service provider | Recipient of Service | Percentage of service tax payable by any person other than the service provider |
| 1 | Taxable services provided or agreed to be provided by any person who is located in a non-taxable territory and received by any person located in the taxable territory other than non-assessee online recipient (OIDAR) | Any person who is located in a nontaxable territory | Nil | Any person located in the taxable territory other than non-assessee online recipient (Business Recipient) | 100% |
| 2 | Services provided or agreed to be provided by a goods transport agency (GTA) in respect of transportation of goods by road | Goods Transport Agency (GTA) | Nil | (a) any factory registered under or governed by the Factories Act, 1948; (b)any society registered under the Societies Registration Act, 1860 or under any other law for the time being in force in any part of India; (c) any co-operative society established by or under any law (d)any person registered under CGST/SGST/UTGST Act; (e) any body corporate established, by or under any law; or (f) any partnership firm whether registered or not under any law including association of persons. (g) Casual taxable person | 100% |
| 3 | Services provided or agreed to be provided by an individual advocate or firm of advocates by way of legal services, directly or indirectly | An individual advocate or firm of advocates | Nil | Any business entity. | 100% |
| 4 | Services provided or agreed to be provided by an arbitral tribunal | An arbitral tribunal | Nil | Any business entity. | 100% |
| 5 | Sponsorship services | Any person | Nil | Anybody corporate or partnership firm. | 100% |
| 6 | Services provided or agreed to be provided by Government or local authority excluding,- (1) renting of immovable property, and (2) services specified below- (i) services by the Department of Posts by way of speed post, express parcel post, life insurance, and agency services provided to a person other than Government; (ii) services in relation to an aircraft or a vessel, inside or outside the precincts of a port or an airport; (iii) transport of goods or passengers. | Government or local authority | Nil | Any business entity. | 100% |
| 7 | Services provided or agreed to be provided by a director of a company or a body corporate to the said company or the body corporate; | A director of a company or a body corporate | Nil | A company or a body corporate. | 100% |
| 8 | Services provided or agreed to be provided by an insurance agent to any person carrying on insurance business | An insurance agent | Nil | Any person carrying on insurance business. | 100% |
| 9 | Services provided or agreed to be provided by a recovery agent to a banking company or a financial institution or a non-banking financial company | A recovery agent | Nil | A banking company or a financial institution or a non banking financial company. | 100% |
| 10 | Services by way of transportation of goods by a vessel from a place outside India up to the customs station of clearance in India | A person located in non-taxable territory to a person located in non-taxable territory | Nil | Importer as defined under clause (26) of section 2 of the Customs Act, 1962. | 100% |
| 11 | Transfer or permitting the use or enjoyment of a copyright covered under clause (a) of sub-section (1) of section 13 of the Copyright Act, 1957 relating to original literary, dramatic, musical or artistic works | Author or music composer, photographer, artist, etc | Nil | Publisher, Music company, Producer | 100% |
| 12 | Radio taxi or Passenger Transport Services provided through electronic commerce operator | Taxi driver or Rent a cab operator | Nil | Any person | 100% by Electronic Commerce Operator |
Source: GST rules
List of goods on which reverse charge is applicable
| S. No | Tariff item, sub-heading, heading or Chapter | Description of supply of Goods | Supplier of goods | Recipient of supply |
| 1. | 0801 | Cashew nuts, not shelled or peeled | Agriculturist | Any registered person |
| 2. | 1404 90 10 | Bidi wrapper leaves (tendu) | Agriculturist | Any registered person |
| 3. | 2401 | Tobacco leaves | Agriculturist | Any registered person |
| 4. | 5004 to 5006 | Silk yarn | Any person who manufactures silk yarn from raw silk or silk worm cocoons for supply of silk yarn | Any registered person |
| 5. | – | Supply of lottery | State Government, Union Territory or any local authority | Lottery distributor or selling agent. Explanation.- For the purposes of this entry, lottery distributor or selling agent has the same meaning as assigned to it in clause (c) of Rule 2 of the Lotteries (Regulation) Rules, 2010, made under the provisions of sub section 1 of section 11 of the Lotteries (Regulations) Act, 1998 (17 of 1998). |
Source: Notification No. 4/2017 Central Tax (rate)
Still has a question? Write a comment below and I will try my best to answer quickly.

